Impact Factor 2024: 1,7
Meine App für die RöFo

Die RöFo ist auch mobil für Sie da. Mit der App können Sie …
… Ihre RöFo bequem zu jeder Zeit und an jedem Ort online und offline lesen. Zum Offline-Lesen laden Sie sich die Ausgaben einfach herunter.
… mit der ausgefeilten Suche schnell und einfach alle Inhalte zu einem Thema finden. Die App enthält auch die vergangenen Ausgaben im Volltext, selbst wenn Sie die Zeitschrift damals noch nicht abonniert hatten.
… auch auf andere Thieme Zeitschriften und aktuelle Thieme Bücher zugreifen, die Sie abonniert bzw. gekauft haben. Die eRef App bündelt für Sie alles übersichtlich an einer Stelle.
Die eRef App ist eine native App für Android und iOS; sie kann mit Smartphones und Tablets genutzt werden.
Interessiert? Dann probieren Sie die neue App doch am besten gleich aus – den Zugriff erhalten Sie unter: www.thieme.de/eref-app
Bei Fragen helfen wir Ihnen gerne: helpdesk@thieme.de
NEWS - DRG

Einladung zum 107. Deutschen Röntgenkongress für medizinische Radiologie und bildgeführte Therapie
Sehr geehrte Damen und Herren, liebe Kolleginnen und Kollegen,
Radiologie verbindet – Menschen, Disziplinen, Technologien und Perspektiven. Sie steht im Zentrum einer modernen, interprofessionellen und datenbasierten Medizin und gestaltet patientenzentriert die Zukunft von Forschung, Lehre und klinischer Versorgung.
Radiologie kennt dabei keine Grenzen – weder fachlich noch räumlich, weder im Denken noch im Handeln. Mit dem Motto „Radiologie grenzenlos" laden wir Sie herzlich zum 107. Deutschen Röntgenkongress 2026 ein – einem Kongress, der bewusst neue Wege geht und die Offenheit sowie Vielfalt unseres Fachs auf allen Ebenen sichtbar macht.
Lesen Sie hier die ganze Einladung.
Sie interessieren sich für Veranstaltungen der DRG?
Dann besuchen Sie den Veranstaltungskalender der DRG
Neues Angebot auf conrad: Knifflige Fälle, die hängen bleiben
Eine Fallsammlung mit 13 einprägsamen Fällen aus dem Berufsleben von Professor Heinz-Jakob Langen ist ab sofort auf der interaktiven Lernplattform conrad der Deutschen Röntgengesellschaft verfügbar. Bemerkenswerterweise hat Langen diese didaktisch wertvolle Sammlung noch vor seinem Eintritt in den Ruhestand erstellt – als Vermächtnis für Ausbildung und Fortbildung in der Radiologie.
Lesen Sie hier ein Gespräch mit Herrn Prof. Langen.
Aktuelle Ausgabe – 09/2025
Bildgebung in der postoperativen Wirbelsäule
Simranjeet Kaur, Radhesh Lalam, Rishi Trivedi
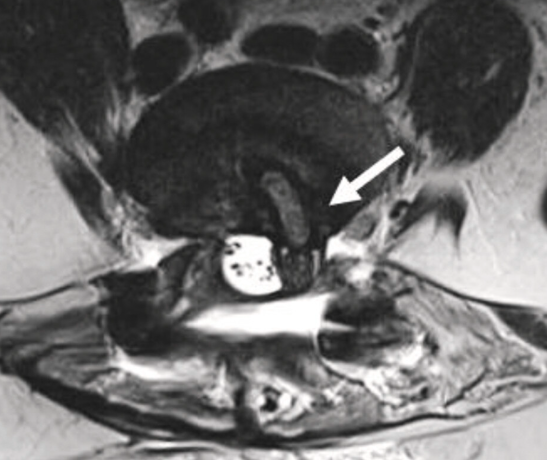
In den letzten Jahrzehnten hat die Zahl der Wirbelsäulenoperationen deutlich zugenommen, entsprechenden ist auch die Zahl der postoperativen Bildgebungsstudien gestiegen. S. Kaur et al. haben eine umfassende Literaturrecherche durchgeführt und verschiedene Richtlinien und Expertenmeinungen zur postoperativen Wirbelsäulenbildgebung berücksichtigt. In ihrer Übersicht stellen sie das normale postoperative Erscheinungsbild dar und erörtern die verschiedenen frühen und verzögerten Komplikationen.Amir Karimzadeh, Wencke Lehnert, Daniel Koehler et al.
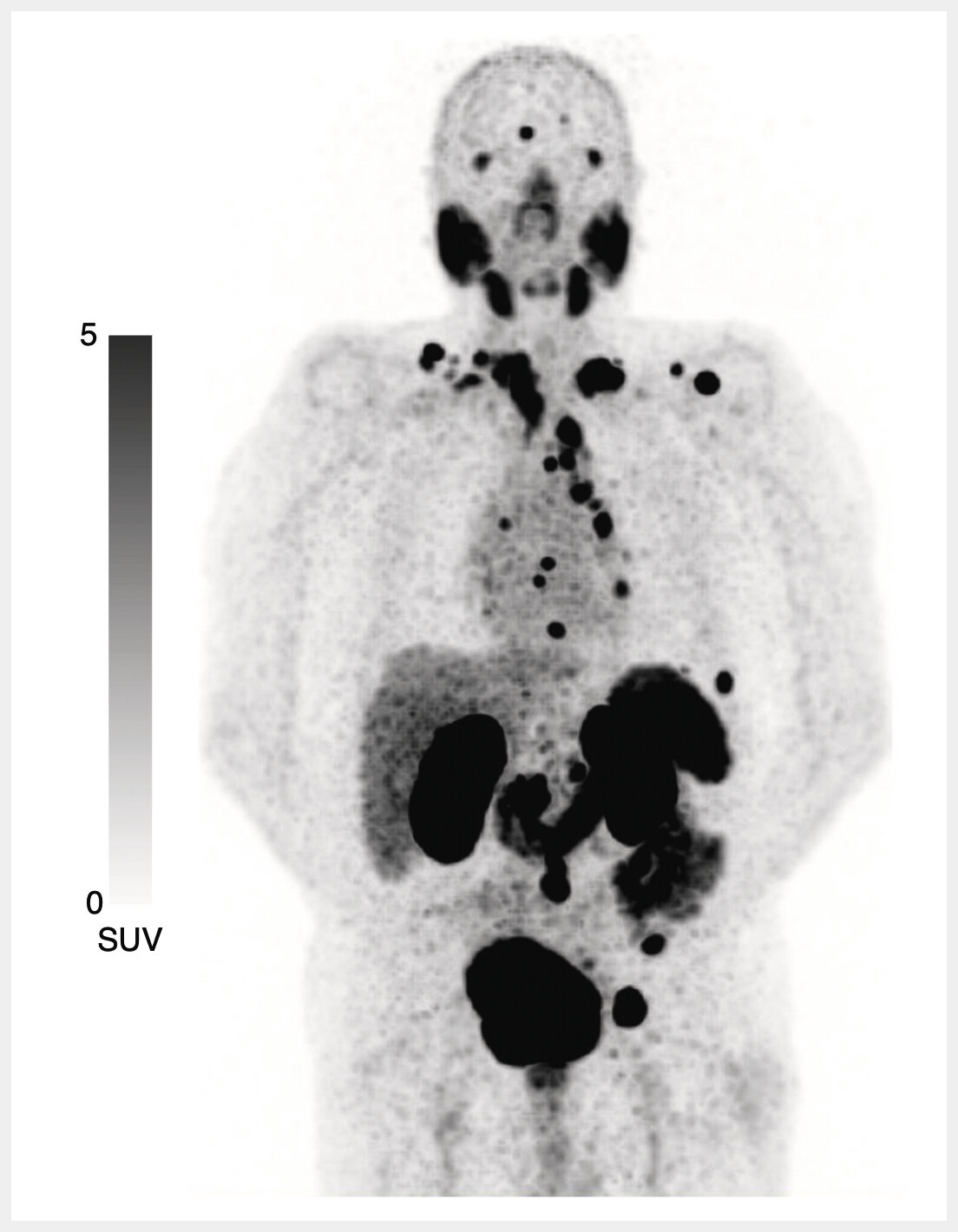
Theranostik in der nuklearen Onkologie kombiniert diagnostische und therapeutische Verfahren unter Verwendung von Radiotracern, um Tumorzellen gezielt anzugreifen. Das prostataspezifische Membranantigen (PSMA) ist eine wichtige Zielstruktur des metastasierten Prostatakrebs, und der Radioligand [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617, der an PSMA bindet, hat vielversprechende Ergebnisse bei der Behandlung von metastasiertem kastrationsresistentem Prostatakrebs (mCRPC) gezeigt. In diesem Review diskutieren A. Karimzadeh und Kollegen die aktuelle Evidenz von [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 bei mCRPC im Kontext ausgewählter Studien und der gemeinsamen EANM/SNMMI-Leitlinien zur Lutetium-177-markierten PSMA-gerichteten Radioligandentherapie.Standardisierte Diagnostik des HCC mit LI-RADS und mRECIST: ein Update zur Situation in Deutschland
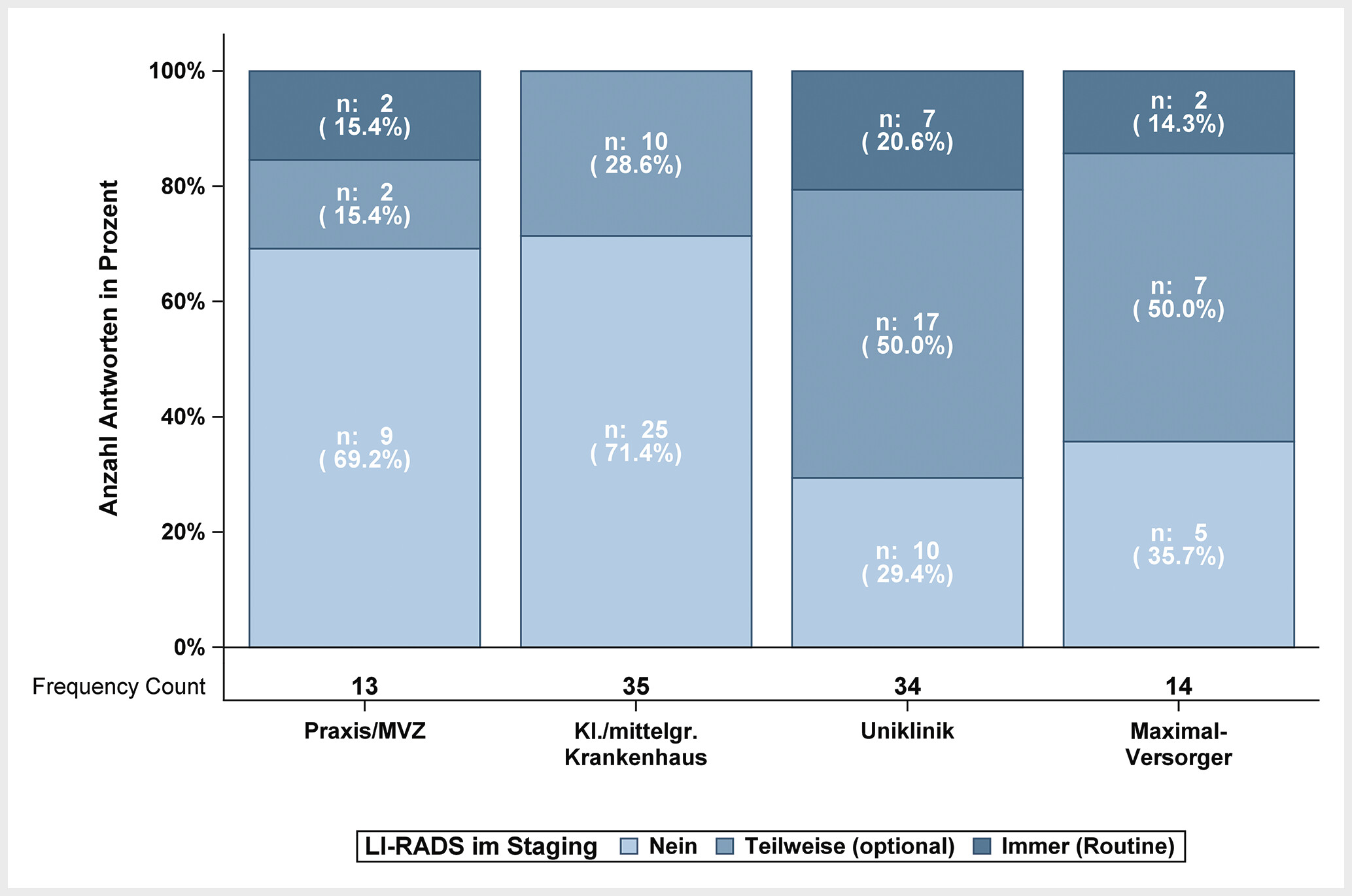
Christian Nelles, Inka Ristow, Markus S. Juchems et al.
C. Nelles und Kollegen haben eine Online-Umfrage zur aktuellen Statuserhebung von CT-Protokollen zur Diagnostik des hepatozellulären Karzinoms (HCC) im Jahr 2023/2024 durchgeführt. Darüber hinaus haben Sie das Nutzungsverhalten strukturierter Befundung mittels LI-RADS und mRECIST erfragt und die Ergebnisse mit einer Umfrage aus 2020 verglichen.